Urban Vertical Farming: Reimagining Real Estate ROI
The real estate landscape is witnessing a revolutionary shift as urban vertical farming takes root in metropolitan areas. This innovative approach to agriculture is not only addressing food security concerns but also reshaping property values and investment strategies. With land scarcity driving prices skyward in urban centers, savvy investors are looking up—literally—to maximize returns on real estate investments.
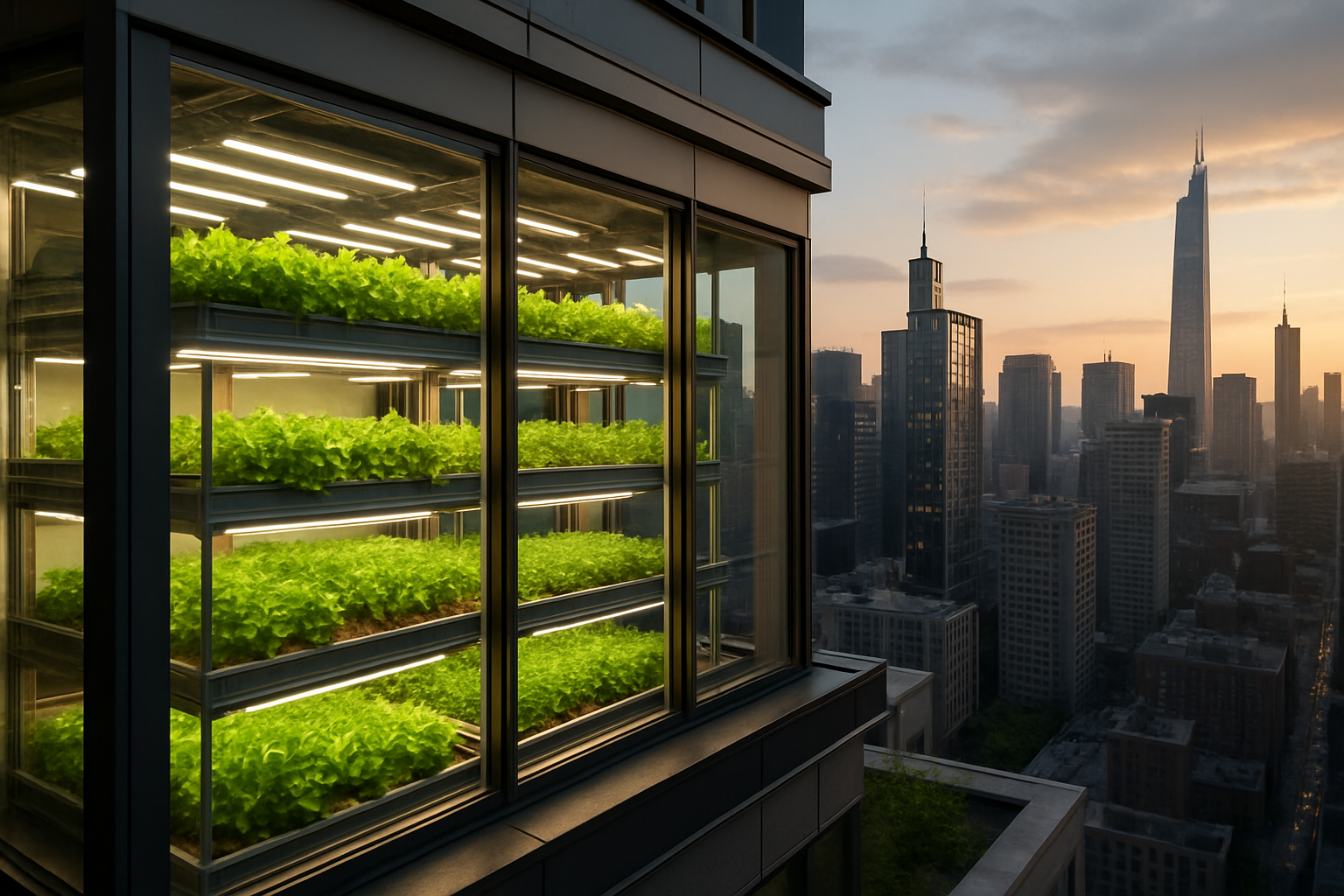

Historical Context and Evolution
The roots of vertical farming can be traced back to the 1915 book by Gilbert Ellis Bailey, titled Vertical Farming. However, it wasn’t until the late 20th century that the idea began to materialize. Dr. Dickson Despommier, a professor at Columbia University, popularized the modern concept in 1999, envisioning skyscrapers filled with floor upon floor of agricultural production.
Real Estate Implications
The integration of vertical farms into urban real estate is transforming property valuation models. Buildings that can support these high-tech agricultural operations are seeing increased demand, potentially leading to higher property values and rental yields. Real estate developers are now considering vertical farming capabilities in their designs, recognizing it as a value-add feature that can attract environmentally conscious tenants and boost ROI.
Financial Landscape and Investment Opportunities
Investors are taking notice of the financial potential in urban vertical farming real estate. Initial capital costs for retrofitting existing structures or constructing purpose-built vertical farms can be substantial. However, the long-term benefits—including consistent crop yields, reduced transportation costs, and premium pricing for locally grown produce—present an attractive value proposition.
Market Trends and Growth Projections
The global vertical farming market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 25.7% from 2021 to 2028, reaching $21.15 billion by 2028. This growth is driven by factors such as increasing urbanization, climate change concerns, and advancements in hydroponic and aeroponic technologies. Real estate investors who position themselves early in this market stand to benefit from this upward trajectory.
Challenges and Considerations
While the potential is significant, investors must navigate several challenges. High energy consumption for lighting and climate control systems can impact operational costs. Additionally, zoning laws and building codes may need to be updated to accommodate these new agricultural spaces within urban areas. Investors should conduct thorough due diligence on local regulations and technological advancements before committing to vertical farming real estate projects.
Impact on Traditional Commercial Real Estate
The rise of urban vertical farming is influencing the broader commercial real estate market. Vacant office buildings and underutilized warehouses are being repurposed for vertical farming, breathing new life into properties that might otherwise struggle to find tenants. This trend is particularly relevant in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, which has left many commercial spaces unoccupied.
Sustainability and ESG Considerations
Urban vertical farming aligns well with Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria, which are increasingly important to investors and consumers alike. Properties that incorporate sustainable farming practices may benefit from improved public perception, potential tax incentives, and alignment with corporate sustainability goals. This can translate to higher occupancy rates and increased property values over time.
Case Studies: Success Stories in Vertical Farming Real Estate
Several pioneering projects demonstrate the potential of vertical farming in real estate. In Singapore, Sky Greens has successfully implemented a low-energy, water-driven vertical farming system in high-rise structures. In the United States, AeroFarms has converted a former steel mill in Newark, New Jersey, into one of the world’s largest indoor vertical farms. These examples showcase how underutilized urban spaces can be transformed into productive agricultural assets.
Future Outlook and Predictions
As technology continues to advance and urban populations grow, the intersection of vertical farming and real estate is expected to expand. We may see the emergence of mixed-use developments that combine residential or office spaces with vertical farms, creating self-sustaining urban ecosystems. This could lead to new property categories and investment vehicles specifically tailored to the urban agriculture sector.
Investor Strategies and Recommendations
For real estate investors looking to capitalize on the urban vertical farming trend, several strategies are worth considering. Partnering with established vertical farming operators to retrofit existing properties can be a lower-risk entry point. Alternatively, investing in the development of purpose-built vertical farming structures may offer higher long-term returns but requires a deeper understanding of the technology and market dynamics.
Conclusion
Urban vertical farming represents a compelling frontier in real estate investment. As cities grapple with food security and sustainability challenges, properties that can support local food production are likely to see increased demand and value appreciation. While the sector is still in its early stages, forward-thinking investors who recognize the potential of this innovative approach to urban agriculture may find themselves well-positioned for significant returns in the evolving real estate landscape.