Predictive Maintenance for Industrial Machinery
Predictive maintenance represents a significant evolution in how industrial machinery is managed, moving beyond reactive repairs and scheduled checks. This advanced approach leverages data and analytical tools to anticipate equipment failures before they occur, optimizing operational efficiency and reducing unexpected downtime across various industrial sectors. By shifting from a fixed maintenance schedule to a data-driven strategy, organizations can enhance the longevity of their assets and improve overall productivity.
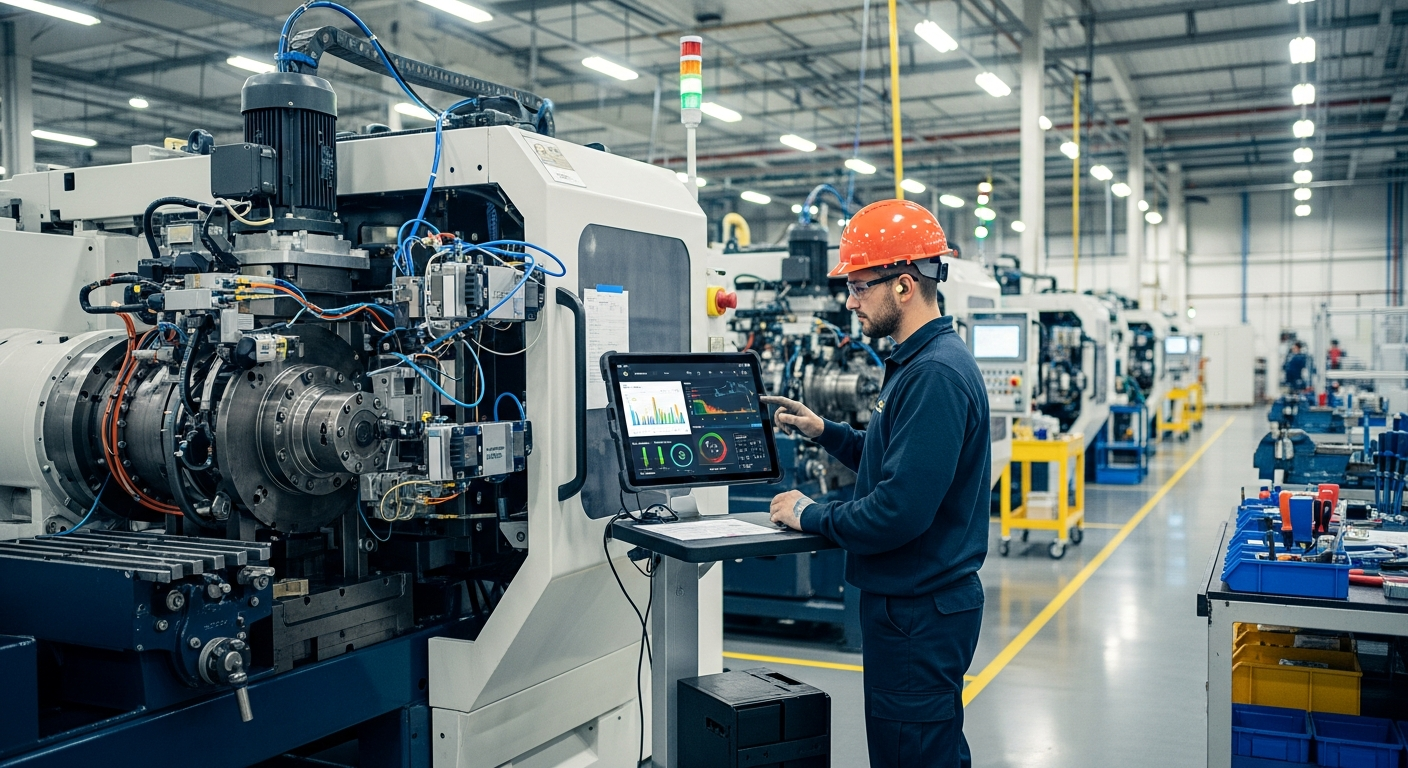

Understanding Predictive Maintenance in Manufacturing
Predictive maintenance is a sophisticated strategy that utilizes data analysis techniques to forecast equipment failures. Unlike traditional reactive maintenance, which addresses issues only after they arise, or preventive maintenance, which relies on fixed schedules, predictive maintenance employs sensors and real-time monitoring to collect data on machine performance. This data, encompassing vibration, temperature, pressure, and other parameters, is then analyzed to detect anomalies and predict potential faults. The goal is to perform maintenance only when it is actually needed, thereby maximizing the operational efficiency of manufacturing processes and reducing unnecessary interventions.
How Digital Technology Drives Efficiency and Production
The integration of digital technology is fundamental to the success of predictive maintenance. Modern industrial operations leverage the Internet of Things (IoT) to connect machinery, allowing for continuous data collection. Advanced analytics, including machine learning and artificial intelligence, process this vast amount of data to identify patterns indicative of impending failures. This technological synergy helps in optimizing production schedules, minimizing costly interruptions, and ensuring consistent output. By foreseeing potential issues, companies can schedule maintenance during planned downtimes, significantly improving overall equipment effectiveness and enhancing the reliability of their entire factory infrastructure.
Implementing Predictive Maintenance: Strategy and Operations
Implementing a predictive maintenance strategy requires careful planning and execution across an enterprise. It typically begins with identifying critical assets that would benefit most from continuous monitoring. This is followed by the installation of appropriate sensors and the establishment of a robust data collection and analysis platform. Training the existing workforce is also crucial, as technicians and operators need to understand the new tools and processes. A well-executed strategy integrates predictive insights into daily operations, allowing for proactive decision-making and efficient resource allocation, ultimately transforming the approach to machinery management.
Benefits for Supply Chain and Logistics
Reliable industrial machinery directly impacts the stability and responsiveness of the supply chain and logistics operations. By preventing unexpected breakdowns, predictive maintenance ensures a consistent flow of goods and materials, reducing delays and improving delivery times. This predictability allows for better inventory management, minimizing the need for buffer stock and optimizing warehouse space. For a global market, maintaining consistent production through robust machinery operations enhances a company’s competitive edge and strengthens its position within the broader supply network.
Cost Considerations for Predictive Maintenance Systems
The initial investment in predictive maintenance systems can vary significantly based on the scale of implementation, the complexity of the machinery, and the level of integration required. Costs typically include hardware (sensors, data acquisition units), software (analytics platforms, cloud services), and professional services for installation, configuration, and ongoing support. While these upfront costs may seem substantial, they are often offset by significant long-term savings through reduced downtime, optimized maintenance schedules, extended asset life, and decreased emergency repair expenses.
| Product/Service | Provider (General Category) | Cost Estimation (Annual/Project) |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Sensor Kits (per machine) | Hardware Manufacturers | $500 - $2,000 |
| Cloud-based Analytics Platform (monthly) | Software Vendors | $100 - $1,000+ (per asset/tier) |
| Full-Service Implementation & Support | Industrial Integrators | $10,000 - $100,000+ (project) |
| Data Scientist/Analyst (salary estimate) | In-house Workforce | $60,000 - $120,000+ (annual) |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Sustainability and Future of Industrial Innovation
Beyond immediate operational and financial benefits, predictive maintenance contributes to greater sustainability in industrial settings. By optimizing equipment performance and extending asset lifespan, it reduces waste associated with premature replacements and inefficient energy consumption. Fewer breakdowns also mean a more stable production environment, which can lead to a smaller carbon footprint. This approach aligns with broader goals of industrial innovation, fostering a culture of continuous improvement and resilience within the existing infrastructure, paving the way for more environmentally responsible and efficient production methods.