Insights into Animal Communication Methods
Animal communication encompasses a vast array of signals and cues exchanged between individuals, crucial for survival, reproduction, and social cohesion across diverse species. From the intricate dances of bees to the complex vocalizations of whales, understanding how animals convey information provides profound insights into their world. These methods vary widely depending on the species, environment, and specific message being transmitted, highlighting the remarkable adaptability and sophistication of life on Earth. Exploring these communication strategies reveals the hidden languages that govern interactions within and between animal populations, offering a deeper appreciation for the natural world.
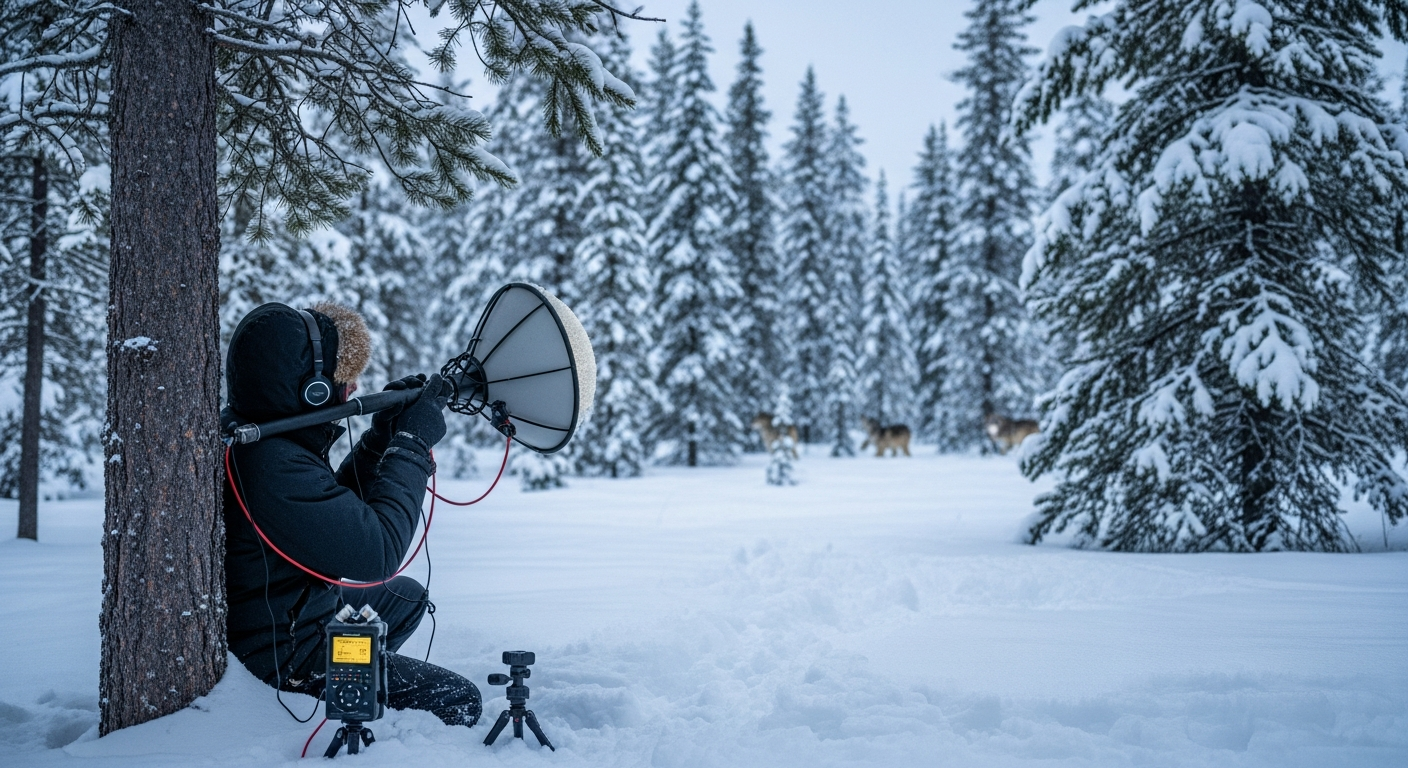

The natural world is rich with diverse forms of communication among animals, a fundamental aspect of their existence. These interactions are not limited to simple calls; they involve a sophisticated interplay of visual displays, chemical signals, tactile exchanges, and electrical impulses. Each method serves distinct purposes, such as warning of predators, attracting mates, locating food, or establishing social hierarchies. By studying these varied approaches, researchers gain valuable insights into animal behavior, cognitive abilities, and their ecological roles. Understanding the nuances of these communication systems is essential for comprehending the intricate relationships that sustain ecosystems globally.
Understanding Diverse Animal Communication Behavior
Animal behavior is intrinsically linked to communication. Many species utilize a combination of signals to ensure their messages are received and understood. Visual signals, for instance, include body postures, facial expressions, and elaborate courtship displays. Birds often use vibrant plumage and complex dances to attract mates, while many mammals employ specific body language to assert dominance or express submission. Chemical communication, involving pheromones, plays a critical role in territorial marking, reproductive signaling, and alarm responses, often traveling silently across vast distances. Acoustic signals, such as vocalizations, chirps, roars, and songs, are prevalent across the animal kingdom, used for long-distance communication, identifying individuals, and coordinating group activities. Tactile communication, involving physical touch, is common in social grooming, parent-offspring bonding, and aggressive encounters, fostering social cohesion or resolving conflicts.
Communication in Wildlife and its Role in Ecosystems
In wildlife, communication is a cornerstone of survival and ecological balance. Wild animals rely on effective communication to navigate their complex environments, find resources, and avoid threats. For example, alarm calls among monkey species can alert an entire group to the presence of a predator, triggering a coordinated escape or defensive response. The intricate communication networks within an ecosystem, from predator-prey interactions to symbiotic relationships, underscore the interconnectedness of all living things. Disruptions to these communication pathways, often caused by human activities like noise pollution or habitat fragmentation, can have cascading effects on wildlife populations and the stability of entire ecosystems. Protecting these natural communication channels is vital for maintaining biodiversity and ecological health.
Species-Specific Communication and Habitat Adaptation
Each animal species has evolved unique communication strategies tailored to its specific habitat and lifestyle. Aquatic animals, such as dolphins and whales, use complex echolocation and varied vocalizations that travel efficiently through water, allowing them to hunt, navigate, and communicate across vast oceanic expanses. Nocturnal animals, like bats, rely heavily on echolocation and scent marking due to limited visibility. Animals living in dense forests might prioritize acoustic signals that can penetrate thick vegetation, while those in open grasslands might favor visual displays. These adaptations highlight the remarkable evolutionary pressures that shape animal communication, demonstrating how environmental factors dictate the most effective ways for species to convey information within their specific niches. Understanding these species-specific nuances is crucial for both scientific study and effective conservation.
The Importance of Communication for Domestic Animal Care and Welfare
For domestic animals, understanding their communication is fundamental to their care and welfare. Pet owners and animal caregivers can greatly enhance the lives of their animals by learning to interpret their signals. A dog’s wagging tail, a cat’s purr, or a horse’s ear position can convey a wealth of information about their emotional state, needs, or discomfort. Recognizing signs of stress, pain, or happiness through their behavior and vocalizations allows humans to provide appropriate responses, prevent behavioral issues, and build stronger bonds. This empathetic understanding contributes significantly to the overall well-being of domestic animals, ensuring they receive the attention, comfort, and medical care they require. Proper interpretation of these signals is a cornerstone of responsible animal ownership and professional animal care.
Animal Communication and its Relevance to Conservation Efforts
Animal communication plays a critical, though often overlooked, role in conservation efforts. By studying how endangered species communicate, conservationists can develop more effective strategies for their protection. For instance, understanding the mating calls of a rare bird can help in identifying suitable breeding grounds or in developing acoustic lures for reintroduction programs. Monitoring changes in communication patterns can also serve as an early indicator of environmental stress or population decline, providing valuable data for timely intervention. Efforts to mitigate human-induced noise pollution, which interferes with acoustic communication, are also integral to protecting sensitive species. Recognizing and preserving the intricate communication systems of wildlife is therefore a key component of comprehensive conservation strategies, helping to ensure the long-term survival of vulnerable species and the health of their habitats.
Understanding the diverse and intricate methods by which animals communicate offers a profound window into their intelligence, social structures, and ecological roles. From the wild expanses of natural habitats to the comfort of domestic settings, these signals shape interactions, facilitate survival, and contribute to the rich tapestry of life on Earth. Continued research into these fascinating systems not only broadens human knowledge but also strengthens the capacity to protect and coexist with the animal kingdom.