Exploring Advancements in Vehicle Safety Systems
Advancements in vehicle safety systems have transformed the automotive landscape, significantly enhancing occupant protection and accident prevention. Modern vehicles integrate a complex array of technologies, from foundational passive safety features to sophisticated active systems, all designed to mitigate risks on the road. This continuous evolution in vehicle technology reflects a commitment to improving overall mobility and ensuring safer transport for everyone, leveraging innovation to create more resilient and responsive driving experiences globally.
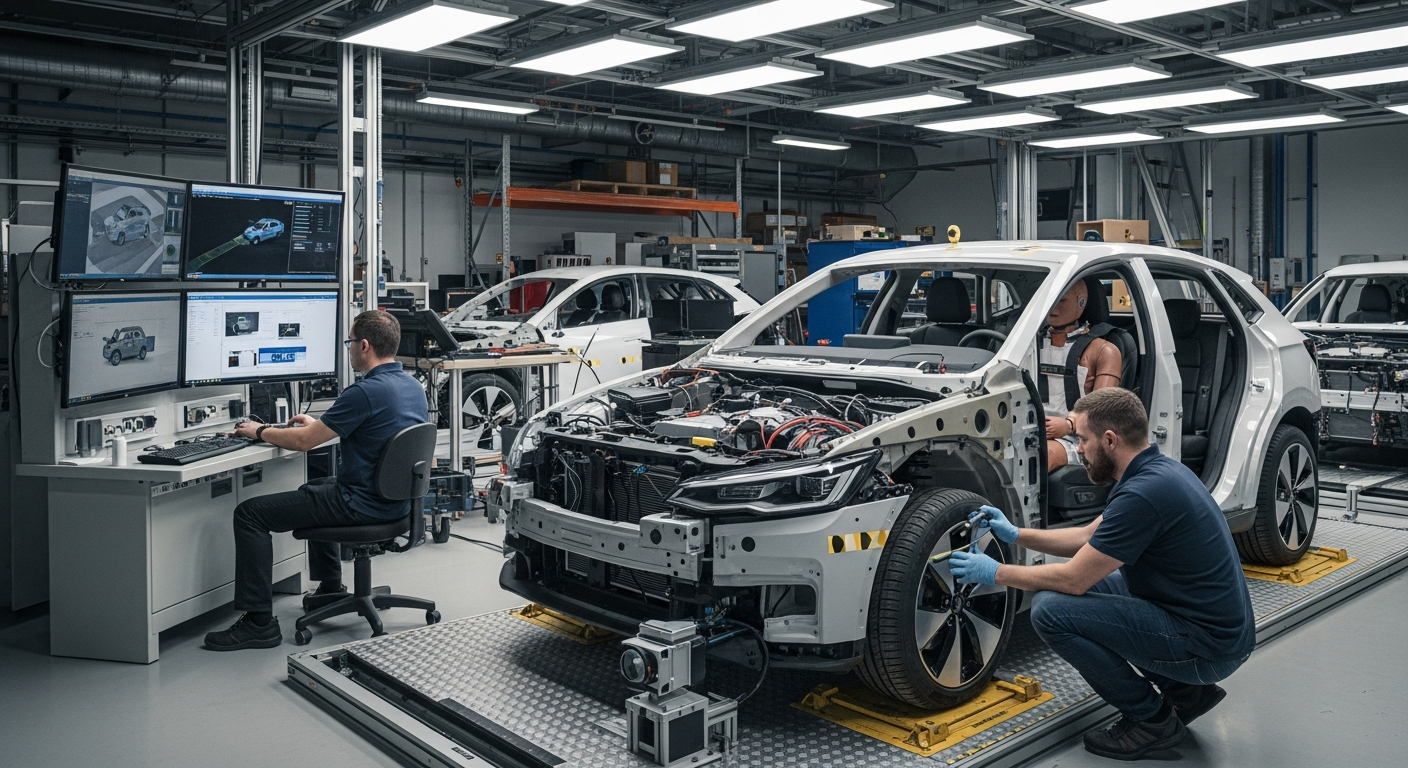

The journey of vehicle safety has seen remarkable progress, moving from basic seatbelts and airbags to highly integrated digital systems. Early safety measures primarily focused on protecting occupants during a collision (passive safety), but contemporary engineering and design principles now emphasize preventing accidents altogether (active safety). This shift is driven by continuous innovation in automotive technology, aiming to create a safer environment for driving and daily transport.
How Has Vehicle Safety Technology Evolved?
Vehicle safety technology has undergone a profound transformation. Initially, passive safety features like seatbelts, crumple zones, and airbags were the primary focus, designed to absorb impact energy and restrain occupants during a crash. Over time, advancements in engineering led to more robust vehicle structures and multi-stage airbag systems. The introduction of anti-lock braking systems (ABS) and electronic stability control (ESC) marked a significant leap, providing drivers with enhanced control during critical driving situations. These innovations laid the groundwork for the sophisticated active safety systems prevalent in modern automotive design.
What Are Key Automotive Innovations in Active Safety?
Today’s automotive industry is characterized by cutting-edge active safety innovations that leverage sensors, cameras, and radar to monitor the driving environment. Features such as automatic emergency braking (AEB), lane-keeping assist (LKA), blind-spot monitoring (BSM), and adaptive cruise control (ACC) actively help drivers avoid collisions. These systems represent a paradigm shift in driving safety, moving towards predictive and preventative measures. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning further refines these technologies, enabling vehicles to make more informed decisions and react faster to potential hazards, thereby improving overall mobility.
How Do Materials and Design Enhance Passive Safety?
The choice of materials and the structural design of a vehicle play a crucial role in passive safety. Modern vehicles utilize high-strength steel, aluminum alloys, and composite materials to create lighter yet more rigid chassis. These advanced materials contribute to enhanced crashworthiness, allowing the vehicle structure to deform in a controlled manner, absorbing impact energy away from the passenger compartment. Innovative design principles, including optimized crumple zones and reinforced cabin structures, work in conjunction with restraint systems to minimize injury risk for occupants. This focus on materials and engineering ensures that vehicles offer robust protection even in severe collisions.
The Role of Connectivity and Infrastructure in Future Mobility Safety
The future of vehicle safety extends beyond individual vehicle systems to encompass connectivity and infrastructure. Vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) and vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) communication technologies are emerging as vital components. These systems allow vehicles to share real-time data about road conditions, traffic, and potential hazards with other vehicles and smart infrastructure elements like traffic lights. This interconnected network aims to reduce congestion, prevent accidents, and improve overall transport efficiency and safety. Such integration is a critical step towards creating a more responsive and safer driving environment for future mobility.
Considering the Future of Electric and Sustainable Transport Safety
The rise of electric vehicles (EVs) and the push for sustainable transport introduce new considerations for safety. While EVs often have a lower center of gravity due to battery placement, enhancing stability, their unique architecture presents challenges in crash scenarios, particularly concerning high-voltage battery protection and thermal management. Future safety engineering must adapt to these new vehicle types, developing specialized protocols for emergency response and designing battery enclosures that maintain integrity during impacts. Innovation in this area is key to ensuring that the transition to electric and sustainable transport models does not compromise the high safety standards established over decades in traditional automotive design.
Insights into Vehicle Safety System Upgrade Costs
Upgrading a vehicle’s safety systems can involve various components, from installing advanced driver-assistance features to enhancing existing ones. The cost can vary significantly based on the type of system, the complexity of installation, and whether it’s an aftermarket addition or an integrated manufacturer upgrade. These systems aim to improve driving safety through technological advancements.
| Upgrade Type | Provider | Cost Estimation (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Blind Spot Monitoring System | Typical Automotive Service Provider | $300 - $800 |
| Rearview Camera System | Typical Automotive Service Provider | $150 - $500 |
| Parking Assist Sensors | Typical Automotive Service Provider | $200 - $600 |
| Dash Cam with Lane Departure | Typical Automotive Retailer | $100 - $400 |
| Advanced Collision Warning | Specialized Aftermarket Installer | $500 - $1500 |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
The ongoing evolution of vehicle safety systems underscores a continuous commitment to protecting drivers, passengers, and pedestrians. From the foundational elements of passive safety to the sophisticated algorithms of active safety, and looking ahead to connected infrastructure and specialized electric vehicle safety, the automotive sector remains dedicated to pushing the boundaries of what is possible. These advancements collectively contribute to a future where driving is not only more efficient and convenient but also significantly safer for all participants in the global transport ecosystem.